HomeRobotic Database - Single Infrastructure | TERRINet


Address: Bessemer Building, Kensington,
London SW7, UK
Website
https://www.imperial.ac.uk/hamlyn-centre/
Scientific Responsible
Guang-Zhong Yang
Robert Merrifield
About
The facility at the Hamlyn Centre for Robotic Surgery consists of state-of-the-art robotic platforms and manufacturing/characterisation devices for the development and construction of the next generation of robotic devices. The Hamlyn Centre makes its robot development facilities, infrastructure and expertise available to institution, local, national the international research communities. The Surgical Robot Challenge is an international annual competition that is organised by the Hamlyn Centre that sees 10 teams come each year from leading robotics institutions around the world to London, to demonstrate their surgical robot innovations to leaders and pioneers of the fields of robotics and surgery. Each team makes use of the unique facilities, infrastructure and expertise in the Hamlyn Centre in the months leading up to the competition and during the competition finals. The Hamlyn Centre also runs Summer and Winter Schools on surgical robotics that each see up to 30 researchers from around the world utilising the equipment and knowhow of the Hamlyn Centre. Furthermore, the Hamlyn Centre runs a leading conference in Medical Robotics called the Hamlyn Symposium, now entering its 11th year that is supported by the unique facilities of the Hamlyn Centre for running surgical robotics demos and hands-on workshops.
Presentation of platforms
Available platforms
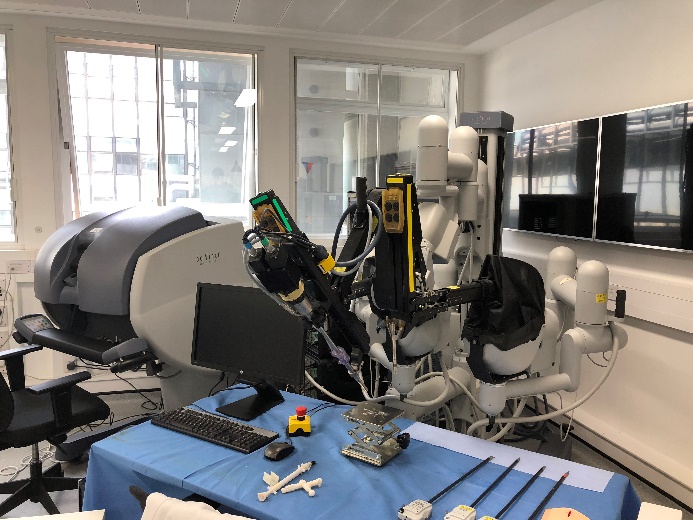

Da Vinci Research Kit (DVRK)
The da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) is a research platform based on the da Vinci Surgical System developed and distributed by Intuitive Surgical Inc. The kit is a collection of first-generation da Vinci components that can be used to assemble a telerobotics platform which provides complete access to all levels of control via open source electronics and software. The platform consists of a surgeon’s console to tele-operate the surgery and a patient side system where the surgery takes place. The surgeon’s console consists of two Master Tool Manipulators, each having 8 DOF for dexterous and natural hand manipulation, and a foot-pedal tray. On the other side at the patient’s end, there are two Patient Side Manipulators, which are controlled by the two Master Tool Manipulators. The interface between the two components is based on custom hardware consisting of motor-controllers, coupled with FPGAs and connected to a PC running the control loops.The DVRK can be exploited for interfacing with different master manipulators, for testing force-feedback strategies, of for the integration on novel tools for surgery.

RAVEN II Surgical Robot
The RAVEN is a proven, third generation surgical robotics testbed that provides the nucleus of an open innovation community. This community is united in the application and support of a common platform, and each member has the power to pursue and develop their own intellectual property. Improvements made by the community to the core robotic manipulator will be made available to the entire group. Individual members then have the opportunity to pursue their own proprietary advances in procedures, attached instruments, supervisory software, and human/machine interfaces.

Motion capture and virtual reality platform
This laboratory is equipped with a state of the art multi-camera motion capture system, various devices for virtual reality immersion, and sporting equipment, ideal for testing wearable robots, body sensor networks and life assistance robots.
User studies in a virtual or real environment can be coupled with an EEG measurement system and motion capture in an open space environment.
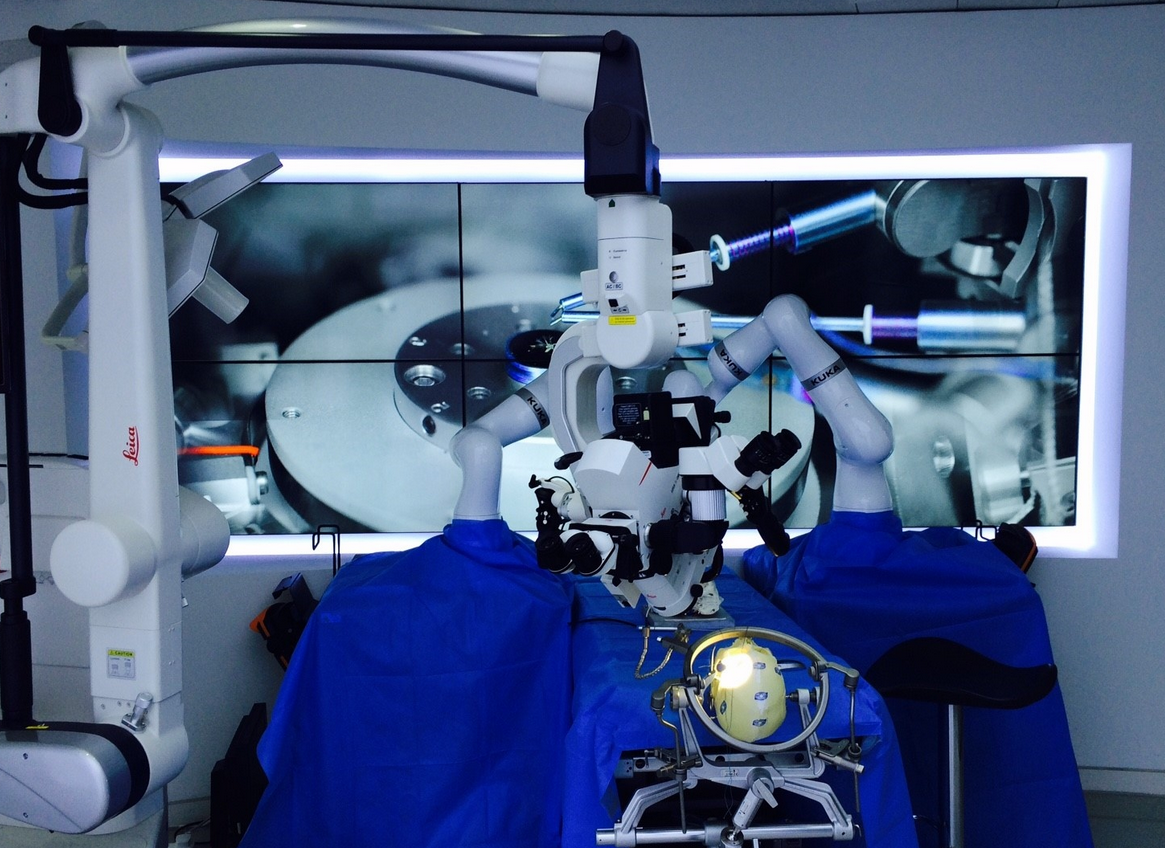
Operation room environment for medical robot prototype
Our operation theatre platform is equipped with various equipment and environment found in operation room specialised in neurosurgery. This platform is equipped with a large number of phantom for simulation of blood vessel, ultrasound and other various body parts and mannequin. Several screen can be used to simulate the feedback that surgeon will get during operation. Various eye tracking system are available for further advanced control and augmented reality applications. Robot control system and haptic devices are available for manipulation study.
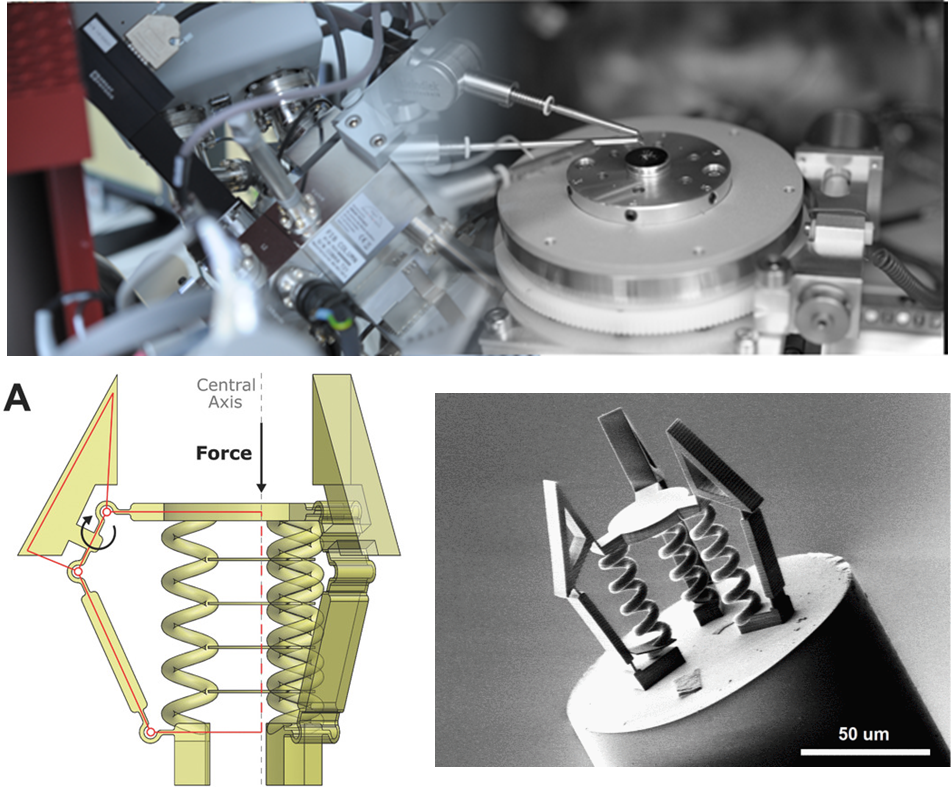
Micro-Robot Fabrication and Characterisation
The Hamlyn Centre Micro-Robot Fabrication and Characterisation platform is articulated around our clean room for microfabrication equipped with a NanoScribe system and expertise in both untethered and tethered microrobots. In addition, a multimaterial fiber platform allows for integration of those tethered robot into complex systems. Precision assembly tools complete the platform. Characterisation tools adapted to those devices allow for full characterisations and development of the prototypes. Finally, various micro and nano manipulation devices, both mechanical and optical, and micro force sensors can be used for the robots actuation and operation.
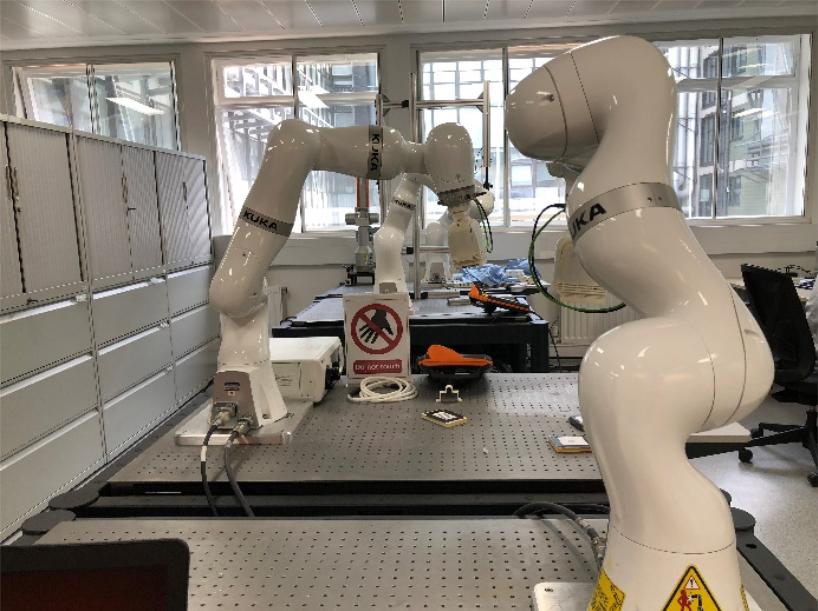

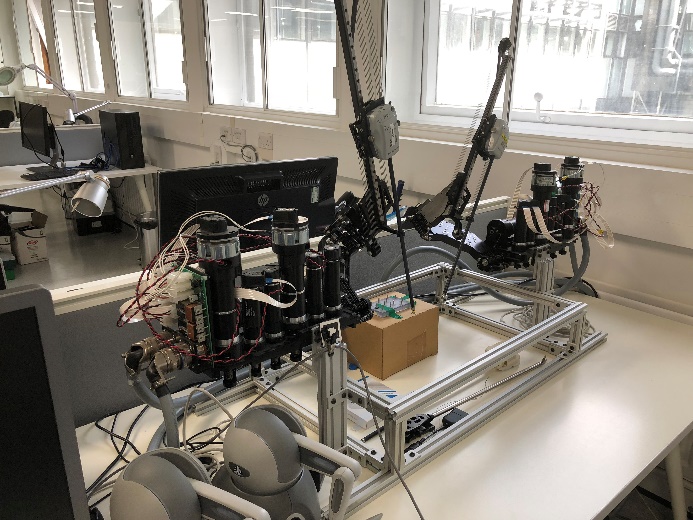
KUKA iiwa7 r800/iiwa14 r820 Platform
The LBR iiwa has integrated, sensitive torque sensors in all seven axes. These endow the lightweight robot with contact detection capabilities and programmable compliance. It masters force-controlled joining operations and continuous-path processes for which the position of the objects must be determined sensitively. It can also handle fragile and sensitive objects without damaging them. In many cases, the integrated sensitivity of the LBR iiwa allows the use of simpler and less expensive tools. The KUKA iiwas are robotic arms with the strength and speed of an industrial robot. It is up to the programmer to set up the appropriate safety settings on the controller, and clear the working environment before testing any code. T1 mode should be used almost exclusively during testing phases to limit the speed of the robot in a safe and reliable way.
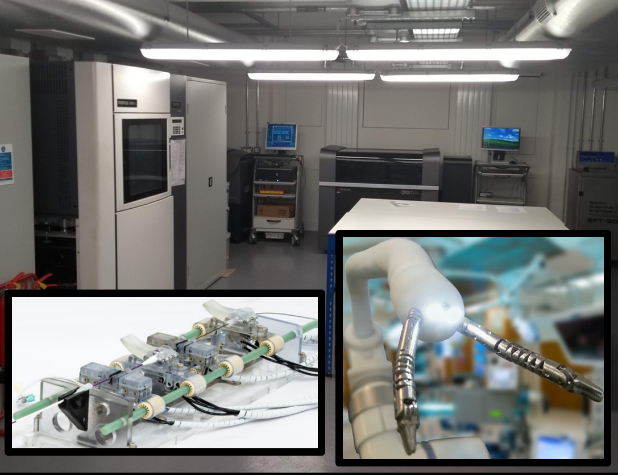

Robotic Fast Prototyping Platform
The robotic fast prototyping platform is a collection of industrial size 3D printing devices and a precision workshop dedicated to the design, fabrication and assembly of robot and medical robots. The fabrication centre comprises several 3D printer with large building volume. The printers are several polyjet printers, FDM printer, SLS metal printer. An electronic lab equipped with pick and place PCB machine allows for large scale fabrication of electronics board. A state of the art workshop and precision manufacturing tool is also available with a micro EDM and 5 axis milling machine. A Clean Room assembly space allows for an assembly complying with medical grade devices. The characterisation platform assure the conformity of the final prototyped both mechanically and electrically in semi-production scale.
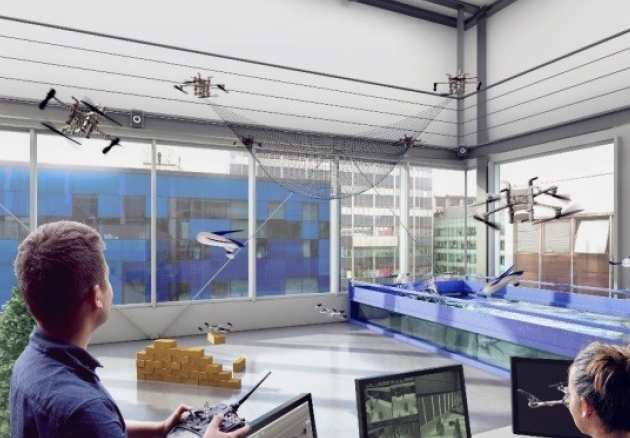

Multi Terrain Flight Arena
A large enclosed 10x6.2x5.5m flight arena (Arena), equipped with 16 Vicon T40 tracking cameras, capable of tracking multiple flying objects in 6 degrees of freedom, with millimetre accuracy. Tracking data can be used for closed-loop control of vehicles. The Arena is the first of its kind in Europe, enabling engineers to test the next generation of aerial robotics for urban environments and extreme conditions. Researchers in the Arena are able to simulate different terrains in the air, the ocean and on land. The space also enables engineers to create extreme conditions such as fire, smoke and heat to simulate how the next generation of drones will perform in harsh environments. The research focus in Arena encompasses two main themes: (i) physical adaptation; (ii) cybernetics adaptation. The physical adaptation includes morphological changes in different environmental conditions for aerial and multi-terrain robots to land, perch, locomote or \"stay still\" in narrow and cluttered spaces. The cybernetical adaptation includes adjustments at the algorithmic level to maintain the stability, avoid the collisions and the track the safe and reliable trajectories. These activities are considered holistically with potential human interactions, neuroscience, and bio-inspiration.